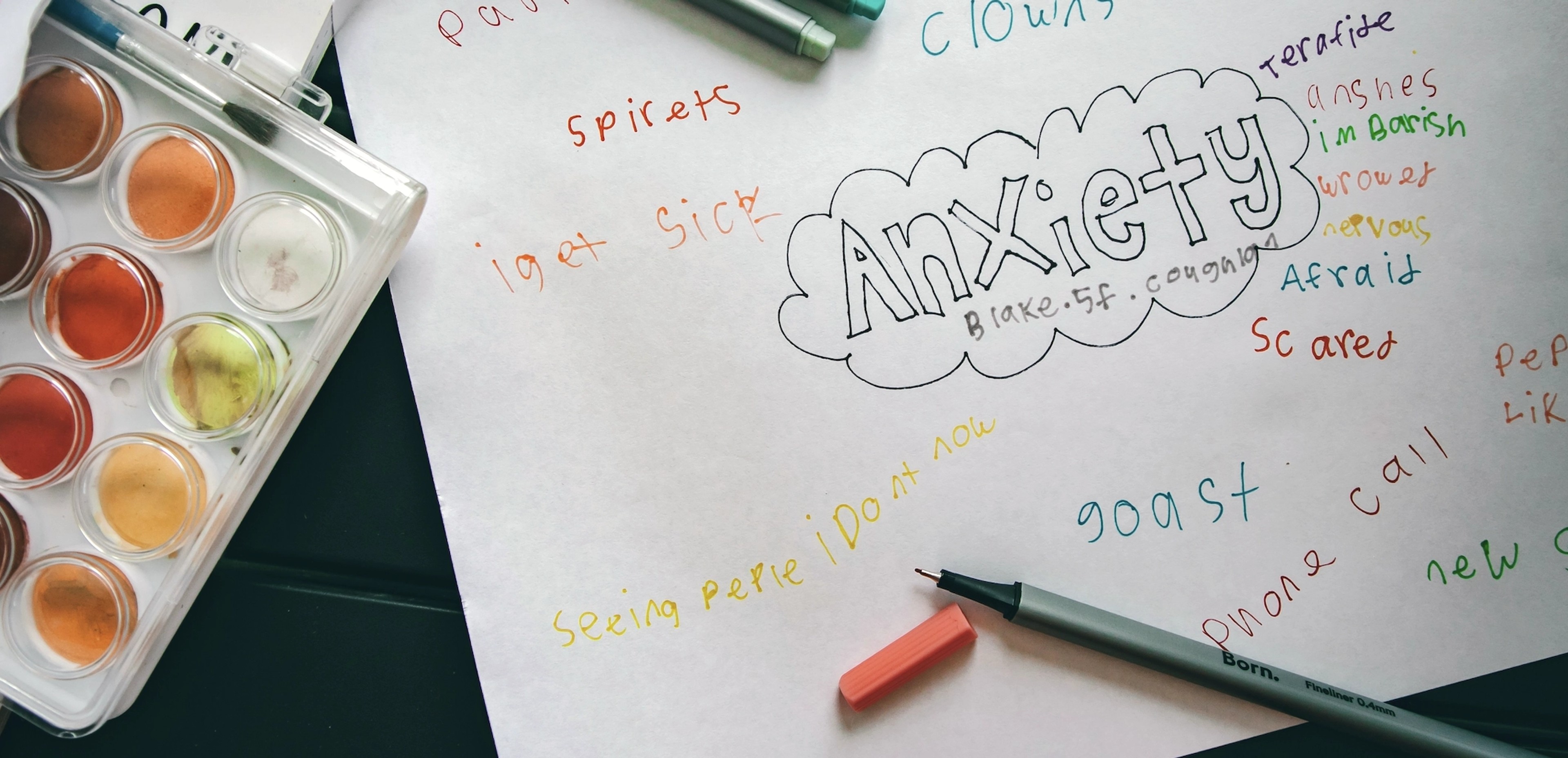Growing Strong Minds: Teaching Emotional Regulation to Set Kids Up for Lifelong Success
By Jenna Galloway, Founder & CEO of Fledge
Helping children develop essential life skills can feel daunting—where do
you even begin? With so much to learn as they grow, it’s all about taking
small, meaningful steps. In this blog, we’ll explore simple, actionable ways
to help your children or students build a strong foundation of emotional
skills, fostering their confidence and resilience along the way.

Helping kids develop emotional regulation skills
Emotional regulation is a cornerstone of mental well-being, influencing how children navigate their relationships, handle stress, and respond to challenges. By teaching kids how to manage their emotions effectively, we
empower them to build resilience and succeed in various aspects of their
lives.
What is emotional regulation?
Emotional regulation refers to a person’s ability to manage their emotions
effectively. For children, it means learning to identify what they’re feeling
and finding appropriate ways to respond. While some emotions like
happiness and excitement are easy to embrace, others like anger or anxiety can be overwhelming without the right tools.
Why emotional regulation matters
Children with strong emotional regulation skills are better equipped to:
- Manage stress They can handle challenges without becoming overwhelmed.
- Build healthy relationships Effective communication and empathy foster better connections with peers and adults.
- Succeed academically Focus and persistence improve when children can regulate their emotions.
- Promote mental health It reduces risks of anxiety and depression, setting a foundation for lifelong well-being.
Why emotional regulation can be challenging for children
Emotional regulation is not an innate skill—it takes time and practice to
develop. For young children, several factors contribute to the difficulty of
managing emotions effectively.
- Brain Development The prefrontal cortex, responsible for
regulating emotions and making decisions, doesn’t fully develop until
the mid-20s. This means that young children have limited capacity to
control their impulses or manage strong emotions. According to the
American Psychological Association, children’s emotional regulation abilities are still maturing, which can lead to reactions like outbursts
or meltdowns (APA, 2022). - Social and Environmental Influences Children are often still
learning how to navigate their social world. Conflicts with peers,
pressure from schoolwork, or challenges at home can heighten
emotional responses. Research by the Center on the Developing Child
at Harvard University shows that chronic stress can interfere with a
child’s ability to regulate their emotions, leading to difficulties in
social and academic settings (Harvard, 2021). - Limited Coping Strategies Unlike adults, children haven’t yet
developed a broad toolkit of coping strategies for managing stress.
Without guidance, they may resort to unhelpful behaviors like
tantrums or withdrawing from others when they feel overwhelmed. A
study by the Child Mind Institute highlights the importance of
teaching children practical strategies, such as deep breathing or
positive self-talk, to cope with difficult emotions (Child Mind Institute,
2020).
Understanding why emotional regulation can be so challenging helps
parents and educators better support children as they develop these
essential skills over time. With patience and guidance, children can
gradually strengthen their emotional resilience, setting them up for greater success in the future.

How can adults support emotional regulation?
- Model emotional awareness Children learn by observing adults. Demonstrate how to name emotions and work through them. For example, saying, “I feel frustrated right now, so I’m taking a deep breath,” can teach them self-regulation strategies in real-time.
- Teach techniques for regulation Simple practices like belly breathing, visualization, or progressive muscle relaxation can help kids calm their minds and bodies. These strategies form the backbone of Fledge’s resources for kids.
- Provide a safe environment Kids feel empowered to express emotions when they feel safe and supported. Create environments at home and school where all emotions are validated and discussed.
- Use play and stories Play-based activities and storytelling are powerful tools for teaching emotional concepts. These methods encourage creativity while reinforcing essential life skills.
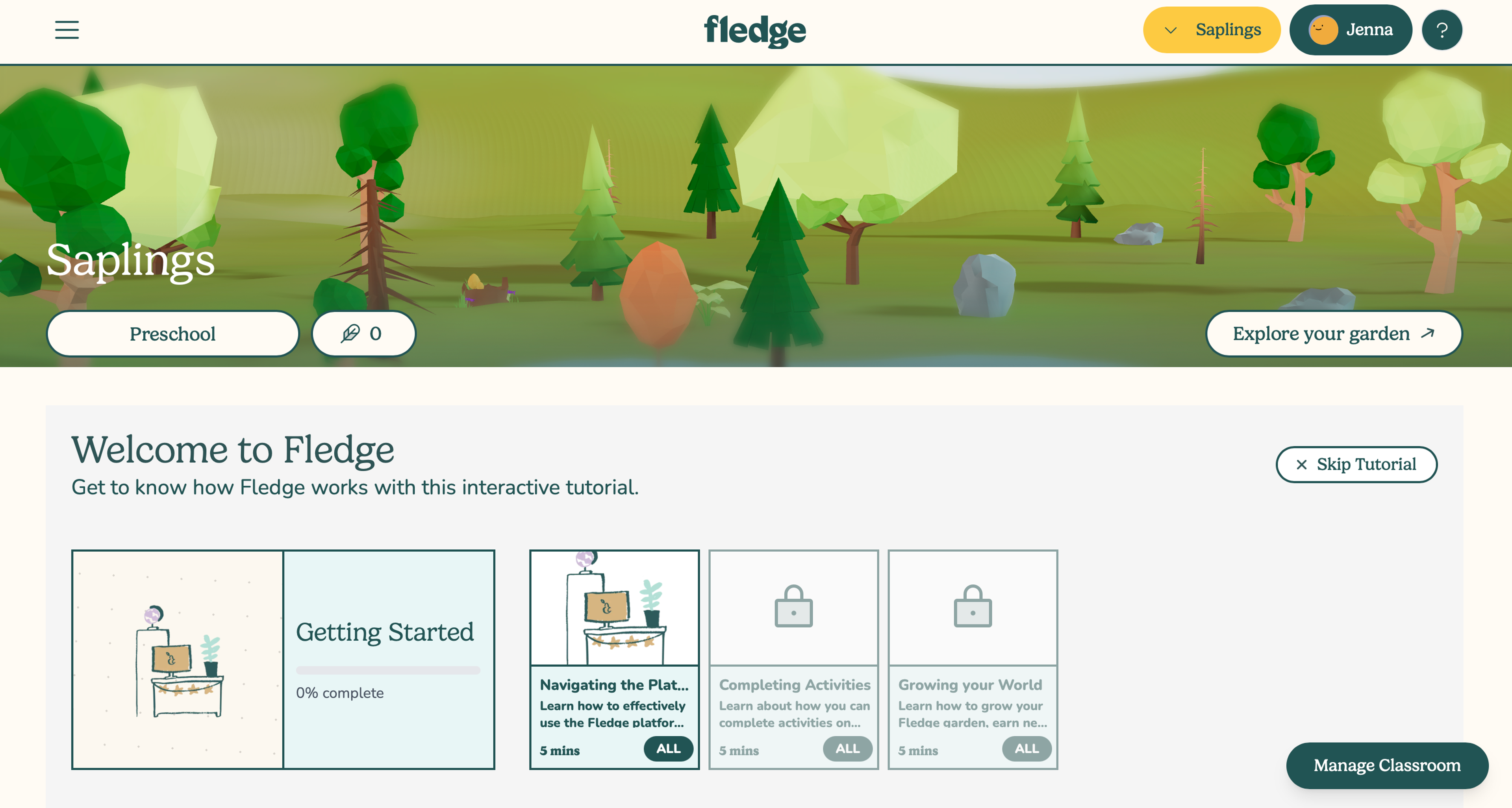
How Fledge helps
The Fledge app equips children, parents, and educators with tools to foster emotional awareness and regulation. By gamifying techniques like belly breathing and mindfulness, Fledge makes learning these skills fun,
engaging, and accessible for children of all ages.
Ready to empower the children in your life?
Explore our presale campaign today—“Buy One, Gift One” is the perfect
opportunity to give the gift of growth to kids and feedback to us so we can
make the app even better!
---
Want more tips on supporting children’s emotional health? Subscribe to our blog for regular insights or contact hello@fledge.health to get access to our “What is Anxiety” module on the platform!